RENEWABLES OVERTAKE FOSSIL FUELS IN THE EU
Canary Media
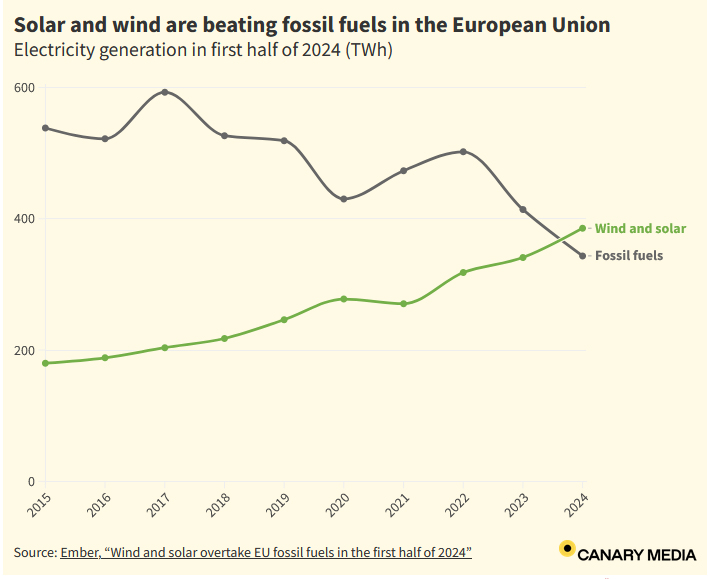
An article from Carrie Klein of Canary Media drew our attention to an encouraging new report from European think tank Ember. The report found that the EU generated more electricity from solar and wind than from fossil fuels in the first half of this year. This is a major milestone, says Klein.
According to Ember, “Reliance on fossil fuel generation reached an all-time low in the first half of this year, even though electricity demand increased and power prices returned to pre-[Covid] levels … Almost half of [EU] Member States generated more electricity from wind and solar than from fossil fuels in the first six months of 2024.”
Their report highlights three key findings:
EU fossil generation fell by 17%: Fossil generation continued to fall to new lows, even as demand rebounded. Fossil fuels generated 17% less in the first half of 2024 compared to the same period in 2023, Coal fell by a quarter (-24%) and gas by 14%. This happened even as demand rebounded by 0.7%, picking up after two years of decline.
Klein writes that this result carried a companion benefit: “Emissions from the power sector have declined in turn, falling by nearly one-third compared to the first half of 2022, an even larger decline than during the Covid-19 pandemic.” According to Ember, this was an unprecedented decline over such a short period.
Wind and solar outpaced the rebound in demand: Wind and solar growth was the single largest driver of the fossil fuel fall, more than exceeding a recovery in electricity demand. Electricity demand rose by 0.7% in the first half of 2024. This marked a reversal from the last two years where demand had fallen amid the gas price crisis, but a mild winter limited the increase. As wind and solar were boosted by structural growth through capacity additions as well as favourable conditions, they more than met the increase in demand to replace fossil fuel generation.
Wind and solar overtook EU fossil generation for the first time: Wind and solar generated 30% of the EU’s electricity in the first half of the year, compared to 27% from fossil fuels. Together, wind and solar surpassed fossil generation in thirteen Member States, with four of these – Germany, Belgium, Hungary and the Netherlands – hitting the milestone for the first time.
Klein says this likely represents a permanent change. “While renewable energy has been growing steadily in the EU for years, that trend kicked into overdrive when Russia invaded Ukraine and disrupted the region’s supply of fossil gas. Energy prices climbed so high following the invasion that electricity demand in the region fell in 2022 and 2023. That pullback hurt fossil fuel generation most of all. Demand is rebounding this year, rising by 0.7 percent over the first six months — and yet fossil fuel generation has continued to fall.”
Klien continues, “The EU’s shift toward solar and wind is also due in part to recently passed permitting reforms, which have allowed renewables to be built and brought online much faster.” She quotes Chris Wright, climate strategy advisor at Ember: “That was the main bottleneck for deploying renewables a few years ago, and it’s in the process of being solved,”
In its report, Ember’s Senior Energy & Climate Data Analyst, Chris Rosslowe, says, “The first half of the year shows fossil generation’s narrowing role in the power sector, and gains for renewables that are beyond temporary variations in conditions. We are witnessing a historic shift and it is happening rapidly.”
Read the Ember report here.
ROUND-THE-CLOCK CLEAN CLEAN ELECTRICITY AND HEAT
400kWe 247Solar Plants deployed at scale
247Solar Plants™ bridge the gap between conventional wind and solar and the need for round-the-clock utility power and industrial-grade heat. 247Solar Plants store the sun’s energy as heat instead of electricity, for 18 hours or more, at much less than the cost of batteries. No generators are required, and 247Solar’s turbines can also burn a variety of fuels, including hydrogen, to ensure 24/7/365 dispatchability.
Extensive Applications
On-grid or off-grid, 247Solar Plants offer a 24/7 alternative to fossil fuels for a broad range of applications:
- CHP: 24/7 low-carbon Combined Heat & Power for industry
- Ultra Heat: Each 247Solar Plant can provide up to 1,500,000 Btu/hr. of heat at temperatures up 1000℃/1800℉ for industrial processes such as cement, glass, steel making, or minerals processing
- Microgrids: Always-on, emissions-free electricity and heat for islands, mines, communities, facilities
- 24/7 baseload power: 24/7 solar electricity, especially for emerging economies
- Green Hydrogen: 24/7 solar electricity and heat to power electrolysis around the clock
- Green Desalination: 24/7 solar electricity and heat to purify water around the clock
ALL ABOUT ELECTROLYZERS
 Electrolyzers are currently the only operational devices for producing green hydrogen. An “explainer” article from Cipher’s Amena Saiyid describes the various types and how they differ.
Electrolyzers are currently the only operational devices for producing green hydrogen. An “explainer” article from Cipher’s Amena Saiyid describes the various types and how they differ.
“When an electrolyzer is powered by clean, renewable energy,” she writes, “it produces carbon-free, or ‘green,’ hydrogen, which can be used to replace emissions-producing fossil fuels in a range of sectors where direct electricity is not a likely option, like steel, cement and shipping.”
Promising varieties
Sayid describes the four main commercial electrolyzer technologies that currently exist:
- “Alkaline electrolyzers are the most widely used and mature machines on the market today, built mostly in China. They are low-cost and can be made with widely available materials. A majority of this type operate at low temperatures and room pressure and are larger in size than other versions of this technology. Such electrolyzers also ramp up to full operating capacity more slowly than other types.
- “Proton exchange membrane (PEM) electrolyzers come in multiple shapes and sizes … PEM electrolyzers can quickly ramp production up and down, but they typically use expensive platinum and iridium that are becoming challenging to source.
- “Solid oxide electrolyzers … can be made with inexpensive materials like nickel and ceramics, making them easier to produce at scale to meet demand. This technology also needs exceedingly high temperatures, ranging from 1,292- to 1,562-degrees Fahrenheit (700-850°C).
- “Anion exchange membrane water electrolyzers fall between alkaline and PEM in terms of cost and can ramp up with renewables output, but their equipment and materials may break down with normal wear-and-tear faster than other types of electrolyzers.”
Sayid writes, “How efficiently each type of electrolyzer uses electricity to produce a kilogram varies.” She cites research by Anne-Sophie Corbeau, global research scholar with Columbia University’s Center on Global Energy Policy, which shows the solid oxide electrolyzer is the most efficient of the four main types. Forgive the shameless plug, but 247Solar technology is capable of producing both electricity and heat up to 970C (1800F), ideal for powering these most-efficient electrolyzers around the clock
Read more about electrolyzers here.
RMI: TWO THIRDS OF ALL ENERGY PRODUCED IS WASTED
Even if burning fossil fuels wasn’t destructive to the environment, it’s still an incredibly inefficient way to produce energy. A post from the Rocky Mountain Institute, excerpted below, shines light on the subject:
Today’s energy system is incredibly inefficient. We waste almost 400 exajoule (EJ) of all energy going into our energy system (two-thirds of total), worth over $4.5 trillion, or almost 5% of global GDP — all before any value is created with energy.
The main culprit is the widespread use of fossil fuels. The majority of energy losses are driven by the inherent inefficiencies of producing and delivering fossil fuels (177 EJ per year), transportation (19 EJ per year), and use (183 EJ per year).
The standout waste is from fossil fuel power plants and Internal Combustion Engines (ICEs). These two technologies combined are responsible for almost half the energy waste globally.
Fossil inefficiency is fossil fragility. Inefficient energy use is vulnerable to more efficient alternatives, as competition by more efficient solutions can deliver more or better services, more conveniently, at lower cost.
We have seen this before. Fossil fuel technologies themselves rose to prominence a century ago through competing on efficiency, pushing out less efficient technology and fuels along the way.
It is happening again. Both more efficient end-use and new clean supply technologies – solar, wind, heat pumps, electric vehicles, and many more – all undercut fossil fuels where they are at their weakest: rampant inefficiency.
The last two sentences are key. They reinforce that it’s not if, but only when and how, the marketplace will end our dependence on fossil fuels.
Read more.
FOLLOW & JOIN 247Solar
Contact: info@247solar.com